Understanding Diverticulosis
Terry Power
Understanding Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is a common condition that affects the colon or large intestine. It occurs when small pouches, called diverticula, develop in the lining of the colon. While these pouches are generally harmless, they can sometimes become inflamed or infected, leading to a more serious condition known as diverticulitis.
For those who desire to serve others and provide quality care, understanding diverticulosis is essential. By gaining knowledge about this condition, healthcare professionals and caregivers can better assist individuals affected by diverticulosis, ensuring they receive the appropriate treatment and support.
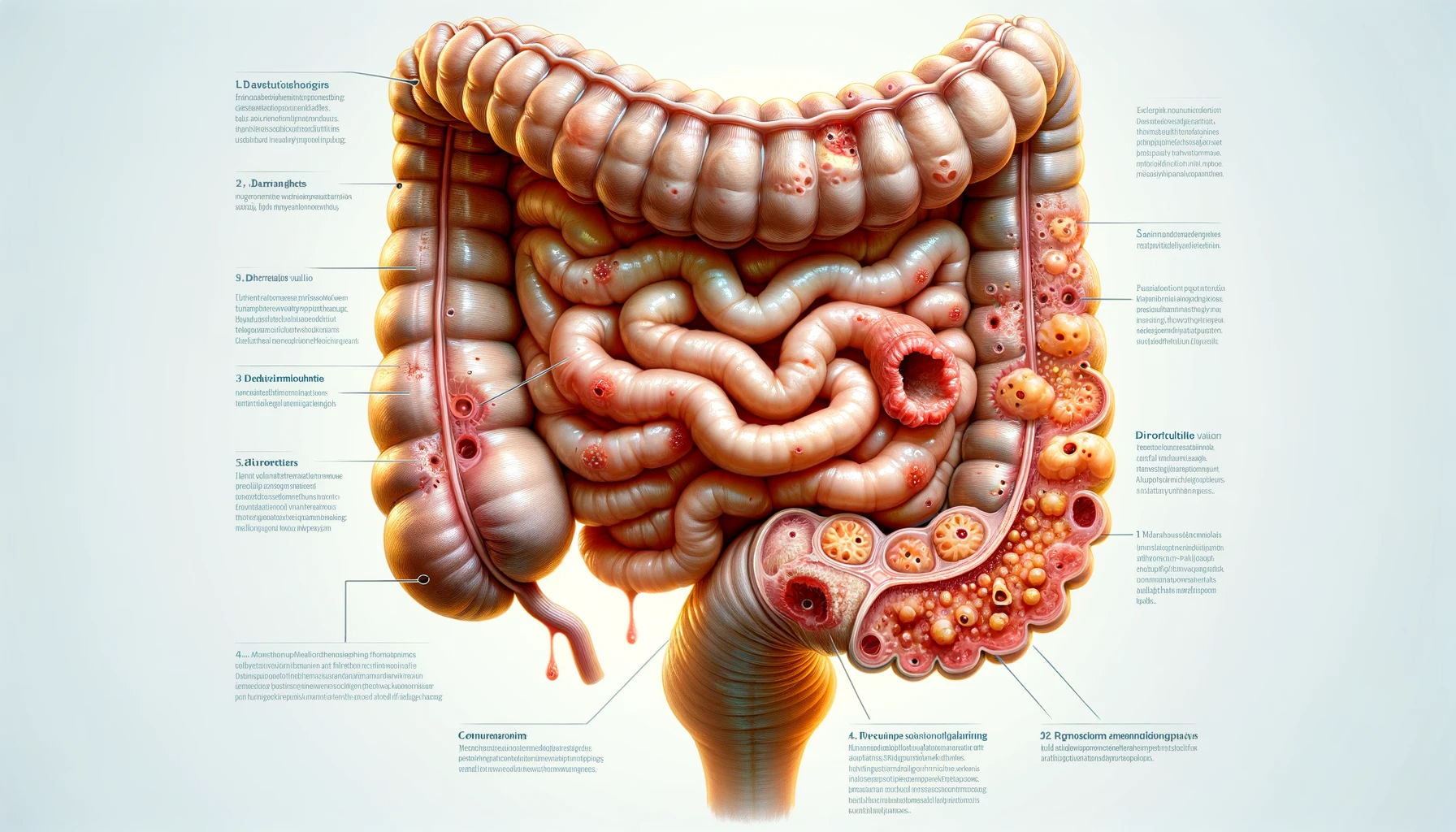
In this guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for diverticulosis. By delving into these topics, we hope to equip caregivers and healthcare providers with the necessary information to provide optimal care and support to individuals with diverticulosis.
What Is Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is a common gastrointestinal condition characterized by the presence of small pouches, or diverticula, in the lining of the colon. These pouches form when the inner layer of the colon bulges outward through weak spots in the outer layer. While diverticulosis itself may not cause symptoms, it can lead to complications such as diverticulitis, inflammation or infection of the diverticula.
Dietary recommendations play a crucial role in managing diverticulosis and preventing complications. A high-fiber diet is often recommended to help maintain regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, which can contribute to the development of diverticula. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Additionally, staying well-hydrated is important to keep stools soft and prevent straining during bowel movements.
Causes of Diverticulosis
There are several risk factors that contribute to the development of diverticulosis. These include dietary risk factors and lifestyle factors. Here are four important factors to consider:
Low-fiber diet: A diet low in fiber can increase the risk of diverticulosis. Fiber helps to add bulk to the stool and prevent constipation, which can put pressure on the colon walls.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing diverticulosis. Excess weight adds strain on the colon, making it more susceptible to developing diverticula.
Lack of physical activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of diverticulosis. Regular exercise helps to promote healthy bowel movements and reduce the risk of developing diverticula.
Smoking: Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of diverticulosis. Smoking can affect the blood vessels in the colon, leading to weakened colon walls.
Symptoms of Diverticulosis
One common indication of diverticulosis is the occasional occurrence of mild symptoms. These symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements. In some cases, diverticulosis may present with more severe symptoms such as rectal bleeding or infection, which can lead to complications. Complications of diverticulosis include diverticulitis, abscess formation, intestinal obstruction, and perforation. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.
To manage diverticulosis, dietary recommendations are often given. A high-fiber diet is commonly recommended to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements, which can help reduce the risk of diverticulosis symptoms and complications. Foods that are rich in fiber include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Additionally, it is important to stay hydrated and to avoid foods that may aggravate the condition, such as spicy or processed foods.
Following these dietary recommendations can help manage diverticulosis and reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosing Diverticulosis
The diagnosis of diverticulosis is typically made through medical imaging tests. Early detection of diverticulosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. Imaging techniques play a vital role in diagnosing this condition, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately identify the presence of diverticula in the colon.
Here are four essential points highlighting the importance of early detection and the role of imaging techniques in diagnosing diverticulosis:
Timely diagnosis enables healthcare providers to initiate appropriate treatment strategies promptly.
Imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans and colonoscopies are commonly used to diagnose diverticulosis.
These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the colon, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize diverticula and assess their severity.
Early detection of diverticulosis can help prevent complications such as diverticulitis, abscesses, and bowel perforation.
Treatment and Prevention of Diverticulosis
Treatment and prevention of diverticulosis involves various strategies aimed at managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. One of the main approaches is making dietary changes. A high-fiber diet is recommended to help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements, which can prevent the formation of diverticula. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
It is also important to drink plenty of water to maintain hydration and aid in digestion. Lifestyle modifications are also crucial in managing diverticulosis. Regular exercise can help improve bowel function and reduce the risk of constipation. Additionally, avoiding smoking and managing stress levels can contribute to overall digestive health.
