Engineering Tech Note. "Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer Reference Design" (Battery/USB powered)
38 views
Skip to first unread message
Jonathan Cline
Feb 8, 2019, 10:32:40 PM2/8/19
to DIYbio
Software, BOM and PCB mask included.
Microchip AN2265 (2016)
OVERVIEW
In medicine, a nebulizer is a drug delivery device that breaks up medical solutions into small aerosol droplets and deliver them directly to the patient’s airways for respiratory therapy. Medical nebulizers are commonly used for the treatment of COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis and other respiratory diseases.
This application note demonstrates an implementation of driving a piezo mesh disk in a vibrating mesh nebu- lizer demo. The demo system features a Microchip 8-bit microcontroller-based piezo mesh disk driver board and a nebulizer plastic housing.
BASICS OF AEROSOL DRUG DELIVERY
According to the American Association for Respiratory Care (AARC), the delivery of aerosolized medication directly to the airways is a mainstay in the emergency treatment and long-term management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and other chronic lung diseases in both the adult and pediatric populations.
VIBRATING MESH TECHNOLOGY
A significant innovation made in the nebulizer market is vibrating mesh technology. Basically, a vibrating mesh nebulizer is composed of a liquid reservoir with a piezo mesh disk mounted on one side of it, and a piezo mesh driver circuit board with batteries. The piezo mesh disk consists of a stainless steel plate that has been perfo- rated with thousands of precision-formed, laser-drilled holes, and surrounded by a piezoelectric material.
The piezoelectric material will vibrate at a very high rate of speed when it is driven by an analog signal of spe- cific voltage, frequency, and waveform that is gener- ated by the driver board. As a result of rapid vibration, solution is drawn through the holes to form droplets of consistent size that are delivered at a low velocity to be be inhaled directly into the lungs.
The vibrating mesh nebulizers offer many advantages when compared to other types of inhalers.
• Nebulize a variety of drugs
• Combine medications, as well as control dosage
• High efficiency with minimal residual medication
volume
• Ease of use for all ages
• Portable, low-power, battery-operated
• Very quiet during operation
• Can be used at home, clinic, hospital or during travel.
One of the challenges of designing a vibrating mesh nebulizer is to generate an adequate and reliable ana- log driving signal, as required to drive a corresponding piezo mesh disk. The piezo mesh disk requires a high voltage waveform at a specific resonant frequency.
NEBULIZER FEATURES
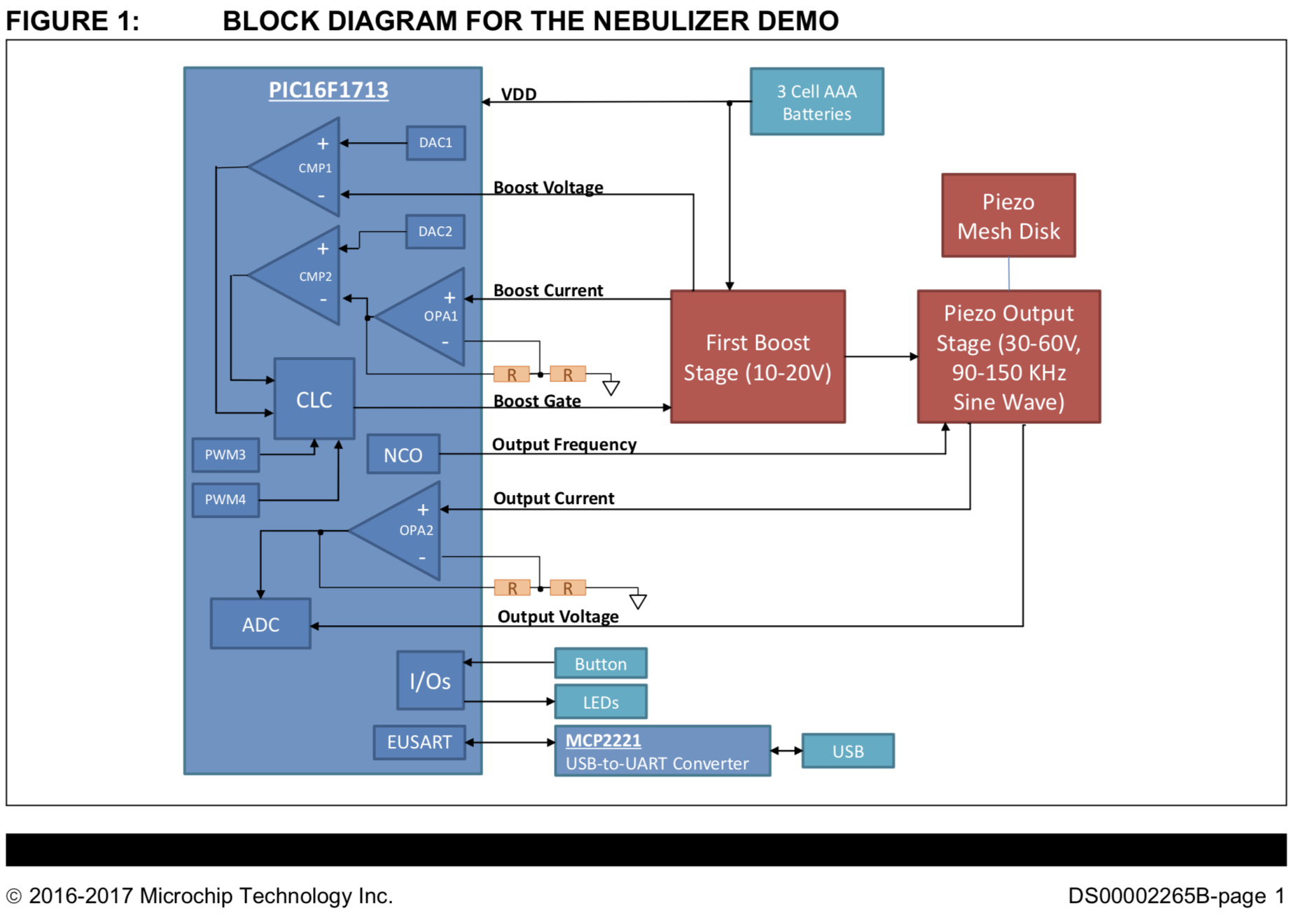
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the nebulizer demo. All of the logic and control is handled within the PIC16F1713 MCU. The power circuitry consists of two functions, a boost stage to generate a higher voltage from the batteries, and an output stage which produces the sine wave to drive the piezo mesh.
Output Stage
The output stage provides the high-voltage sine wave drive signal for the piezo mesh disk. It is a boost topol- ogy as well, so it does provide gain over the bulk volt- age from the boost stage. The output MOSFET is driven by the Numerically Controlled Oscillator (NCO), which provides a variable frequency with a fixed 50% duty cycle. The fine adjustment range of the NCO allows the output stage to be tuned to the particular piezo device attached to the nebulizer.
Because the output stage is a boost topology, the piezo mesh disk can be driven both high and low with a single MOSFET. The MOSFET will pull the piezo low, and when MOSFET is turned OFF, inductor L2 becomes a current source that drives the piezo high. Inductor L3 converts what would be a sharp falling edge when the MOSFET turns ON into sine wave as it forms a reso- nant circuit with C4 and the piezo mesh disk. C3 is a DC blocking cap that keeps the voltage on the piezo symmetrical and prevents the DC voltage on VBOOST from affecting the piezo when you are not driving the output.
Reply all
Reply to author
Forward
0 new messages
